4.1
Bulk Carrier: a bulk carrier
is a cargo ship intended for carriage of dry bulk cargoes such as
grain, coal, ore, etc., provided with topside tanks at both shoulders
and bilge hoppers in both double bottom wings in the cargo space.
Below is a typical midship section
and general arrangement .
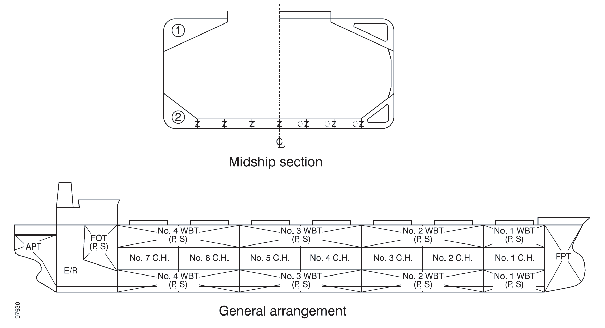
Figure 1 Typical midship section and general arrangement
4.2
Topside tank: tanks provided
in cargo spaces at both shoulders as the space (1) shown in the drawing
above.
4.3
Bilge hopper: a conventional
bulk carrier has hopper structures at the both bottom wings in cargo
holds. This part of cargo hold is called "bilge hopper". Double bottom
tanks in way of bilge hopper are often called "bilge hopper tank".
In the diagram, the space is shown as (2).
4.4
Girder and floor in double bottom: provided
in double bottom tanks, "girder" usually indicates a strong frame
usually with the full depth provided in ship's longitudinal direction.
The girder fitted on the center line is called "center girder", while
the others are called "side girders". "Floor" means strong framing
in ship's transverse direction provided in double bottom. In double
bottom beneath cargo holds, floor plates are usually solid ones with
full depth of the tank. In this regard, solid ones are called "solid
floors" distinctively from the others.
4.5
Transverse web in topside tanks: strong
framing provided in topside tanks in transverse direction, also called
"transverse ring". Of a transverse ring in a topside tank, the part
supporting the upper deck is called deck transverse, the part attached
to the side shell is called side transverse and the part attached
to the bottom is called (topside) bottom transverse.
4.6
Transverse web in bilge hopper tanks: strong
framing provided in the transverse direction in a bilge hopper tank.
Transverse webs are called "bilge hopper transverse", "side transverse"
and "bottom transverse" in accordance with the name of the hull members
to which they are attached.
4.7
Framing of various kinds: on
a typical bulk carrier, framing
is designed as a longitudinal system in topside and double bottom
tanks and as transverse system at cargo hold side shell. Framing fitted
in ship's longitudinal direction is called "longitudinals". To identify
them in detail, the name of the plate they are attached to is added
such as "deck longitudinals", "side longitudinals", "bottom longitudinals",
etc. Framing attached to the side shell in the cargo holds are called
"hold frames", "side frames", "main frames", "shell frames", etc.

Figure 2 Typical cross section of cargo ship (bulk carrier)