When the craft enters service, safety assessment does not stop. It is
important that a management system is in place that ensures that all those aspects
identified in the safety assessment relating to operational procedures, regular checks
and maintenance tasks are implemented so that safety standards can be upheld. The
appropriate mechanism for this is provided by the International Safety Management (ISM)
Code, requiring the operator to implement a Safety Management System (SMS). The SMS
should incorporate results from the PSSA and SSA, in particular with reference to:
-
.1 crew operational procedures;
-
.2 emergency procedures and actions;
-
.3 procedures related to the control of hazardous
situations and accidents;
-
.4 maintenance procedures for equipment whose sudden
failure may have a hazardous or catastrophic effect;
-
.5 inspection intervals and methods; and
-
.6 control of documents and data relevant for the SMS
as well as the integrity and operation of the craft.
Table 1 – Correlation between levels of probability and categories of effect
| Probability(quantitative)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10-0
|
10-3
|
10-5
|
10-7
|
10-9
|
| Probability
(descriptive)
FAA
|
Probable
|
Improbable
|
Extremely
Improbable
|
| JAA
|
Frequent
|
Reasonably
Probable
|
Remote
|
Extremely
Remote
|
| Category
of Effect
|
Minor
|
Major
|
Hazardous
|
Catastrophic
|
| Effect on craft, occupants and
environment
|
- slight reduction in safety
margins or functional capabilities; or
- slight increase in
crew workload; or
- some inconvenience to
occupants
|
- significant reduction in
safety margins or functional capabilities; or
-
significant increase in crew workload; or
-
discomfort to occupants; or
- possibly injuries to
occupants; or
- localized structural damage; or
- moderate environmental pollution
|
- large reduction in safety
margins or functional capabilities; or
- large increase in
crew workload, so that the crew may not be able to perform tasks
accurately or completely; or
- serious or fatal
injuries to a relatively small number of occupants; or
- large structural damage; or
-
significant environment pollution
|
- loss of craft; or
- multiple fatalities;
or
- large environmental pollution with long-term
effects
|
Table 2 – SSA verification data sheet
| SSA
verification data sheet
|
Sheet____ of ____
Issue :
Date
:
|
| FHA/PSSA
requirement
|
Implemented
design
|
| No.
|
Failure condition
|
Objectives
|
Event
|
Probability
|
SSA/FTA reference
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 3 – Input function list
| List of
functions worksheet
|
Sheet____ of ____
Issue :
Date
:
|
| Function No.
|
Function
|
System
Subsystem
Equipment
|
Equipment- ID-No.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 4 – FHA worksheet
| Functional
hazard analysis worksheet
|
Sheet____ of ____
Issue :
Date
:
|
| System:
Subsystem:
|
Function:
|
| Item No.
|
Failure condition
|
Mission phase
|
Failure effects
|
Classification
|
Objectives
|
Remarks
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 5 – Component FMECA worksheet
| Component
FMECA worksheet
|
Sheet____ of ____
Issue :
Date :
|
| System:
Subsystem:
|
FTA reference:
|
| Item No.
|
Item
|
Item Failure mode
|
Mode Failure rate
|
Mission phase
|
Failure effects
|
Detection method
|
Classification
|
Remarks
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 6 – FMES worksheet
| FMES
worksheet
|
Sheet____ of ____
Issue :
Date
:
|
| System:
Subsystem:
|
| Item No.
|
Failure mode
|
Failure rate
|
Effects on system
|
Failure cause (FMECA
Ref.)
|
Detectability
|
Remarks
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 7 – Zonal Hazard Analysis data sheet
| ZHA: Hazard Identification data sheet
|
Sheet____ of ____
Issue :
Date
:
|
| System:
Zone:
Zone
number:
|
System:
Equipment:
|
Subsystem:
|
| ID
|
Hazardous element
|
Hazardous condition
|
Initiator event
|
Effects
|
Probability
|
Safety measures/ Means of
compliance
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
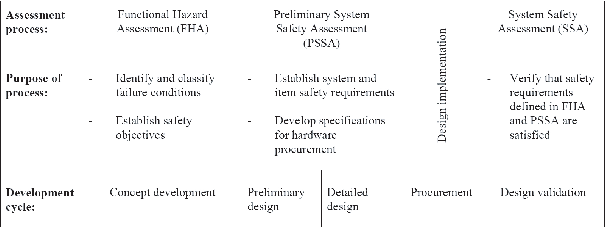
Figure 1 – Relationship between safety assessment processes and the different phases
of the development cycle