
Section
7 Welding qualification requirements for high strength steel for special marine
applications

7.1 Goal-based framework
7.1.1 The purpose of this Section is to present a goal-based approach to the
requirements for high strength steels for special marine applications, not covered
elsewhere in the Rules for the Manufacture, Testing and Certification of Materials, July 2022. Whilst the primary intent of
the application of the welding qualifications listed herein is for pressure
vessels/submersible craft intended for human occupancy, use and application of these
qualifications for other constructions may be specially considered within the scope
of the goal-based framework.
7.1.2 The goals, functional requirements and performance requirements listed herein relate
to welding qualifications required to be performed for construction.
7.1.3 In addition to this goal-based framework, the relevant requirements of
the Rules for the Manufacture, Testing and Certification of Materials, July 2022 are to be complied with for certification.
In order to satisfy the goal-based framework in this Chapter, it is necessary to
comply with the other applicable Rules related to materials, manufacture, testing,
survey and classification.
7.1.4 The list of goals is as follows:
- Welding qualifications shall demonstrate that the resulting
weld joints have the integrity to minimise the risk of loss of the structure due
to failure.
- Welding qualifications shall demonstrate that the resulting
welds minimise the hazard to persons, assets or environment in any foreseeable
operating conditions.
7.1.5 The list of functional requirements (FR) is as follows:
- Welding procedure qualification tests shall demonstrate
acceptable chemical and mechanical properties for the application and withstand
the applied design loads.
- Welds produced in accordance with a qualified weld procedure
and by qualified welders shall be able to function in a safe and acceptable
manner, for compliance with the manufacturing and design criteria.
7.1.6 The list of performance requirements (PR) is as follows:
- For welding procedure qualification tests, the mechanical
properties for category A and B welds shall comply with the requirements stated
in Table 12.7.1 Mechanical property acceptance
requirements for butt welding in plate (in welds that form part of the pressure
hull boundary, and tensile loading under normal submarine operation) for
applicable Material Class Special Application 1 and 2.
- When required by a specific project or specified testing
regime, the surface crack extension from flawed bulge explosion (FBE) tests is
to be not greater than 50 mm. Where indications of laminar flaws are detected
within 10 mm of the tension surface, and they extend to within 50 mm of the
fatigue cracked notch, then there is the potential for them to have influenced
the shock loading of the bulge panel flaw. In such cases the FBE test is not
considered valid.
- When required by a specific project or specified testing
regime, four of the five crack tip opening displacement (CTOD) test results must
be greater than 0,1 mm. One value may be less than 0,1 mm provided it is greater
than 0,07 mm.
- For welding procedure qualification tests, the mechanical
properties for category C and D welds shall comply with the requirements stated
in Ch 12, 2 Welding procedure qualification tests for steels except that Charpy impact test minimum energy
requirements are to meet the requirements of Table 12.7.1 Mechanical property acceptance
requirements for butt welding in plate (in welds that form part of the pressure
hull boundary, and tensile loading under normal submarine operation) for
applicable Material Class Special Application 1 and 2.
- For welder qualification tests, the results from visual
inspection and non-destructive examination (NDE) are to be in accordance with
Ch 12, 2.5 Non-destructive examination (NDE) 2.5.5.
- Welders shall demonstrate that they can consistently meet
the above requirement.
Table 12.7.1 Mechanical property acceptance
requirements for butt welding in plate (in welds that form part of the pressure
hull boundary, and tensile loading under normal submarine operation) for
applicable Material Class Special Application 1 and 2
| Material Class (Special Application)
|
Tensile test
|
Charpy V-notch impact tests
|
|
Yield strength (N/mm2)
See Note 1
|
Elongation (%)
(minimum)
|
Test
temperature (°C)
|
Average absorbed energy (J)
(minimum)
See Note 2
|
Average Charpy impact crystallinity (%)
(maximum)
See Note 3
|
| High Strength
Steel – Special Application 1
|
>550
|
16
|
−50
|
>50
|
55
|
| High Strength Steel – Special Application 2 (undermatched weld)
|
>565
|
16
|
-50
|
50
|
55
|
| High Strength Steel – Special Application 2 (Matched weld)
|
>690
|
16
|
-50
|
50
|
55
|
|
Note 1. The individual reduction of area and tensile strength
values together with weld metal chemical analysis are recorded
for information only.
Note 2. No individual value may be less than 40 J.
Note 3. No
individual value may be greater than 70 per cent.
|

7.2 LR accepted solutions for welding qualifications for high strength steel for special marine applications
7.2.1 The requirements of this Section relate to the welding qualifications of high
strength steels intended for use in special marine applications, which are not
covered elsewhere in this Chapter.
7.2.3 The application, in entirety, of the prescriptive content in this Section (including
any references leading out) is considered to meet the listed goals.
7.2.5 The requirements presented herein represent an accepted solution for
welding qualifications, certified for use High Strength Steel – Special Application
1 and 2, and the appropriate consumable grade for the relevant material class.

7.3 General requirements
7.3.3 Welding procedures for High Strength Steel – Special Application 2 may
be approved with a weld metal strength lower than the minimum specified for the base
material, i.e. undermatched welding. Where welding procedures are approved for
undermatched welding, the requirements specified in Ch 13, 10.3 General requirements 10.3.5 are to be
followed.

7.4 Welding procedure qualification tests
7.4.1 Welding procedure qualification tests are to be performed to qualify
welding for specific categories, as defined by Table 12.7.2 Weld categories of high
strength steel for special marine applications.
Table 12.7.2 Weld categories of high
strength steel for special marine applications
| Category
|
Description
|
| A
|
Weld forms part of the pressure hull boundary and must withstand
explosive loading.
|
| B
|
Weld must withstand tensile loads under normal submarine
operation.
|
| C
|
Welds in frames and frame to pressure hull welds. These welds may
experience shock loads but do not form part of the pressure hull
boundary (i.e. their failure would not compromise watertight
integrity).
|
| D
|
Welds in secondary structure where none of the above categories
apply.
|
7.4.3 High Strength Steel – Special Application 2 butt weld applications are to be
qualified via Category A and B routes. Fillet weld applications may be qualified via
Category C and D routes.
7.4.4 A test assembly in accordance with Figure 12.7.1 Butt welds in plate (category
A and B) is to be prepared and sectioned for mechanical
testing. The assembly is to simulate production conditions including minimal
restraint and in the worst position. Panels welded in the vertical up position will
automatically qualify the procedure for all positions.
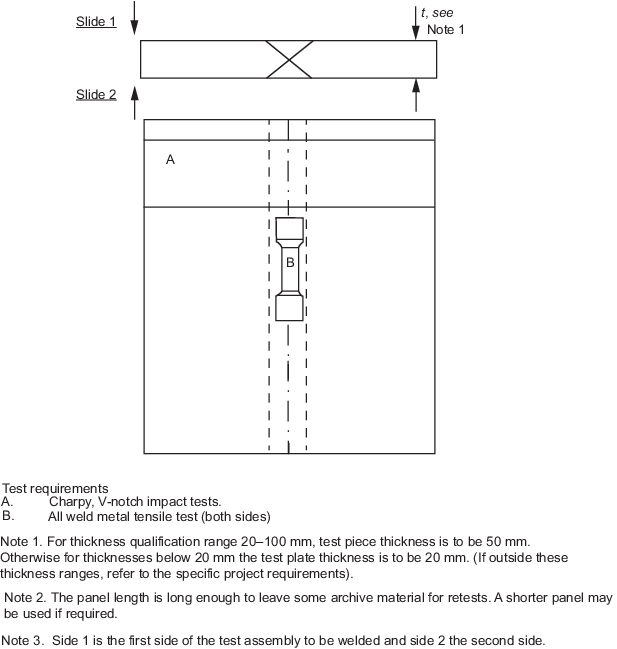
Figure 12.7.1 Butt welds in plate (category
A and B)
7.4.5 Two sets of Charpy V-notch impact tests are required, notched in the weld
centre. One set is to be taken from 2 mm below the surface of side 1 and one set
from 2 mm below the surface of side 2.
7.4.6 The Charpy V-notch impact fracture appearance is to be determined in
accordance with ISO 148-1 or another recognised National Standard.
7.4.7 All weld tensile samples are to be taken from both sides of the weld.
The test specimens are to be of a circular cross- section, seeCh 11, 2.1 Dimensions of test specimens 2.1.1. Where necessary, reduced size test samples in accordance with
ISO 6892-1: Metallic materials – Tensile testing – Part 1: Method of test room at
temperature or other recognised National Standard are permitted to ensure
samples are extracted wholly within the weld metal.
7.4.8 When the procedure is for thin plates, below 20 mm, the Charpy V-notch
impact and tensile requirement is to be taken from the mid-section of the weld.
7.4.11 FBE tests are to meet the following requirements:
- Test specimens are to be notched in the side of the weld
exhibiting the highest average crystallinity (i.e. Charpy V-notch impact
specimens must be tested and analysed before the FBE can be notched).
- Tests are to be carried out at −5°C.
- The resulting depth of bulge for the test to be valid
must be at least 12,5 mm.
7.4.12 Number of specimens and method of testing for FBE is to be agreed with the
project authority.
7.4.14 Two sets of five crack tip opening displacement test specimens are
required. One set is to be notched in the first side of the weld and one set notch
in the second side of the weld. Both sets of specimens are to be notched in the weld
centre. For 20 mm thick test plate the dimensions are to be W = 40 mm,
B = 20 mm and the notch is to be through the weld thickness and 20 mm
deep. For the 50 mm test plate they are to be no less than 45 mm square with a crack
depth to width ratio (a/W) of 0,3. Tests are to comply with Ch 2, 6 Crack tip opening displacement tests and
tested at −5°C.
7.4.16 For category A and B welds, any change in the following will require a
new test piece and requalification:
- Process: Any change in the process from that
used to weld the test plate.
- Edge preparation:
- Any change from two-sided welding to full
penetration butt welds made from one side only.
- Any change in the location of the root greater
than 2 mm which would bring it to within 15 mm of either plate
surface.
- Any change which results in a single plane
fusion line through the thickness when this was not previously (for
category 1 only).
- Consumable:
- Any change in the wire or electrode used for the
root weld of full penetration butt welds made from one side or if
the root is located within 15 mm of the plate surface and the root
is not removed by back gouging or grinding.
- Any increase in wire or electrode diameter.
- Parent material:
- Any change in parent material, except for the following
permissible conditions:
- It is permissible to use a welding procedure
approved for welding High Strength Steel – Special
Application 1 to weld High Strength Steel – Special
Application 2, where High Strength Steel – Special
Application 2 is to be welded with undermatching weld
metal.
- It is permissible to use a welding procedure
approved for welding High Strength Steel – Special
Application 2 using undermatching weld metal to weld High
Strength Steel – Special Application 1.
- Any change from either matched to undermatched, or
undermatched to matched welding, for High Strength Steel, Special
Application 2.
- Any change in plate thickness above or below 20 mm
- Heat Input:
- Any change in heat input beyond the limits used
to weld test assemblies.
- Any increase in the number of welding heads
feeding the weld pool.
- Current: Any change of current or change of
polarity.
- Interpass temperature:Any increase in the permitted
interpass temperature.
- Equipment:
- Any change in the power source characteristics,
i.e. change from constant voltage to constant current or vice
versa.
- Any change in pulse generation for when pulse
current is used.
- Any change to use multiple head welding
devices.

7.5 Welding procedure specification (WPS)
7.5.1 A WPS for High Strength Steel – Special Application 2 which is approved
for undermatched welding, shall specify the maximum root gap for which the WPS is
applicable. This gap should be set prior to completion of the qualification test and
in consultation with the project authority. The requirements specified in Ch 13, 10.3 General requirements 10.3.5 are to be followed, in
addition if actual production welding root gaps are greater than as specified in the
WPS, the project authority should be consulted.

7.6 Welder qualification
7.6.1 The test plate thickness is to be no less than 20 mm with the exception that fillet
weld test piece is to have a standing test piece of 16 mm, a passing member of equal
or greater thickness and a leg length of 11 mm. Mild steel plates may be used in
place of high strength steel plates.
7.6.4 To retain a qualification, the welder shall have one weld examined using
both radiography and ultrasonic examination, every six months.
|