
Section
2 Materials

2.1 Materials

2.2 Protection of steelwork

2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates
2.3.1 This Section provides the requirements for crack arrest design to reduce
the risk of brittle fractures in container ships where thick steel plates are applied
for longitudinal structural members in the upper deck region. The upper deck region
comprises upper deck plating, hatch side coaming plating, hatch coaming top plating and
attached longitudinals.
2.3.2 This Section is to be applied to container ships where the steel plates for
longitudinal structural members exceed a thickness of 50 mm but are not greater than 100
mm. Special consideration is required for plates with a thickness exceeding 100 mm.
2.3.4 Where steel having specified minimum yield strength of 460 Nmm2 is utilised
the material grade is to be EH.
2.3.5 The approach in this Section generally applies to the erection
block-to-block joints. Appropriate measures are to be considered to prevent large scale
fracture of the hull girder in anticipation of the following:
-
Crack initiation in the block-to-block butt weld joint in either the
hatch side coaming or upper deck. Crack propagates along the butt weld joint
without deviation.
-
Crack initiation in the block-to-block butt weld joint in either the
hatch side coaming or upper deck. Crack propagates away from the butt weld joint
running into base metal.
-
Crack initiation in any welded joint, for example in way of
attachment welds, and deviates away from the butt weld joint running into base
metal.
2.3.6 The detailed arrangements for crack arrest design are to be submitted for
approval.
2.3.8 Where Measure 1 is required in Table 8.2.1 Preventative measures to be used
in design and construction for thick steel plates, 100 per cent ultrasonic testing in accordance
with Ch 13, 2.12 Non-destructive examination of steel welds of the Rules for the Manufacture, Testing and Certification of Materials, July 2022, both application and acceptance criteria, is to be carried
out on all block-to-block butt joints of all upper flange longitudinal structural
members in the cargo hold region. Upper flange longitudinal structural members include
the topmost strakes of the inner hull/bulkhead, the sheer strake, main deck, coaming
plate, coaming top plate, and all attached longitudinal stiffeners. These members are
defined in Figure 8.2.1 Upper flange longitudinal
structural members.
Table 8.2.1 Preventative measures to be used
in design and construction for thick steel plates
Nominal
yield
strength
(N/mm2)
|
Thickness
of hatch coaming plating see Note 3 & 4
(mm)
|
Measure, see Note 1
|
| 1
|
2
|
3 +
4
|
5
|
| 355
|
50 < t ≤
85
|
Not required
|
Not required
|
Not required
|
Not required
|
| 85 < t ≤
100
|
Required
|
Not required
|
Not required
|
Not required
|
| 390
|
50 < t ≤
85
|
Required
|
Not required
|
Not required
|
Not required
|
| 85 < t ≤
100
|
Required
|
See Note
2
|
Required
|
Required
|
| 460
|
50 < t ≤
100
|
Required
|
See Note
2
|
Required
|
Required
|
| Key to
measures:
|
| Measure 1:
|
NDE
during construction on all upper flange longitudinal members, see
Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.8
|
| Measure 2:
|
Periodic
in-service NDE, see
Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.10
|
| Measure 3:
|
Either
block shift, or crack arrest insert plates, or crack arrest holes or
enhanced NDE, see
Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.9
|
| Measure 4:
|
Crack
arrest steel for the upper deck, see
Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.11
|
| Measure 5:
|
Crack
arrest steel for the upper deck, see
Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.12
|
|
Note 1. Measures are to be
applied where 'Required' is shown.
Note 2. Measure 2 may be
required where enhanced NDE during construction has been applied as part
of Measure 3
Note 3. Hatch coaming
plating includes side plating and top plating
Note 4. Use of steels with thickness greater than 100mm will be specially
considered
|
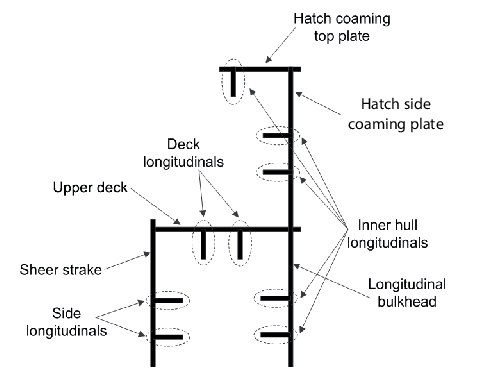
Figure 8.2.1 Upper flange longitudinal
structural members
2.3.10 Where Measure 3 is required in Table 8.2.1 Preventative measures to be used
in design and construction for thick steel plates, the following are
considered to be acceptable examples of brittle crack arrest design for the case given
in Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.5.(a):
-
Where the block-to-block butt welds of the hatch side coaming plate
and those of the upper deck are staggered, this offset is to be greater than or
equal to 300 mm. This offset distance is defined in Figure 8.2.2 Minimum offset between
block-to-block butt welds of the hatch side coaming and those of the upper deck
staggered. Brittle crack arrest steel, as defined
in Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.14, is to be provided for the hatch side coaming
plate.
-
Where crack arrest holes are provided in way of the block-to-block
butt welds at the region where the hatch side coaming weld meets the deck weld,
see
Figure 8.2.3 Crack arrest hole in way of the
block-to-block butt weld at the region where hatch side coaming weld meets the deck
weld, the corners of the crack arrest holes
located where the hatch side coaming joints meet the deck weld are to be specially
assessed for fatigue strength. The fatigue strength is also to be assessed at the
location where the block-to-block butt weld intersects the crack arrest hole.
Brittle crack arrest steel, as defined in Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.14, is to be provided for the hatch side coaming
plate.
-
Where higher crack arrest steel insert plates such as SUF (Surface
Layer with Ultra-Fine grain) steel or equivalent, or weld metal inserts with high
crack arrest toughness properties are provided in way of the block-to-block butt
welds at the region where hatch side coaming weld meets the deck weld. Brittle
crack arrest steel, as defined in Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.14, is to be provided for the hatch side coaming
plate.
- As an alternative to the mechanical measures (i.e.
block offset, or crack arrest inserts, or crack arrest holes, or high arrest
toughness welds), with the provision of crack arrest steel for the hatch coaming side
plate stipulated in Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.10.(a), Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.10.(b) and Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.10.(c), enhanced non-destructive examination can be carried out in
association with stricter acceptance criteria. The acceptance criteria are to be
determined in accordance with Chapter 2 of the ShipRight Procedure for the Use of
Enhanced NDE in Container Ships,and the enhanced NDE is to be carried out in
accordance with Chapter 3 of the ShipRight Procedure for the Use of Enhanced NDE
in Container Ships. For areas of the weld which are inaccessible for enhanced
NDE, alternative NDE procedures using the same acceptance criteria as the enhanced
NDE are to be agreed with LR as described in the ShipRight Procedure for the Use
of Enhanced NDE in Container Ships. The weld toughness of the block to block
butt welds of the hatch coaming side plate, hatch coaming top plate and upper deck is
to be as required by Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.13 and EGW welding is not permitted.
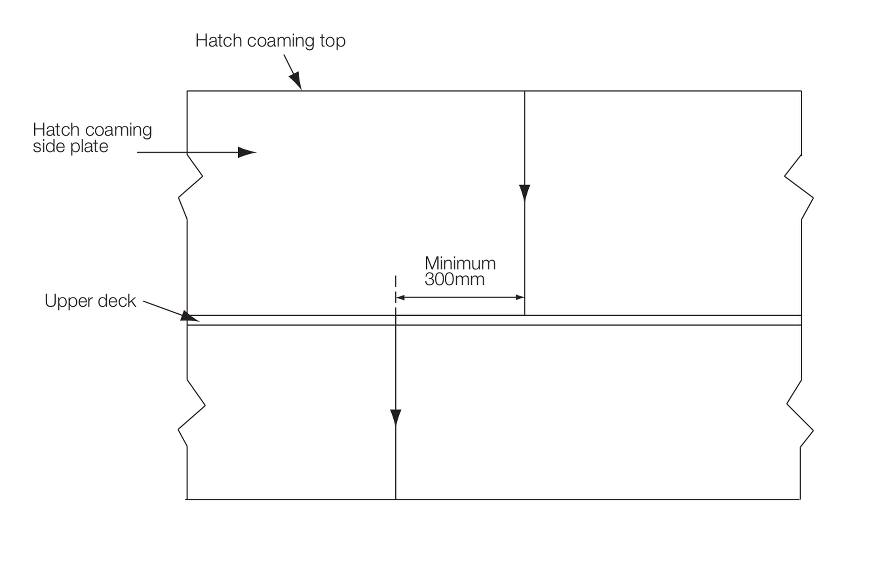
Figure 8.2.2 Minimum offset between
block-to-block butt welds of the hatch side coaming and those of the upper deck
staggered
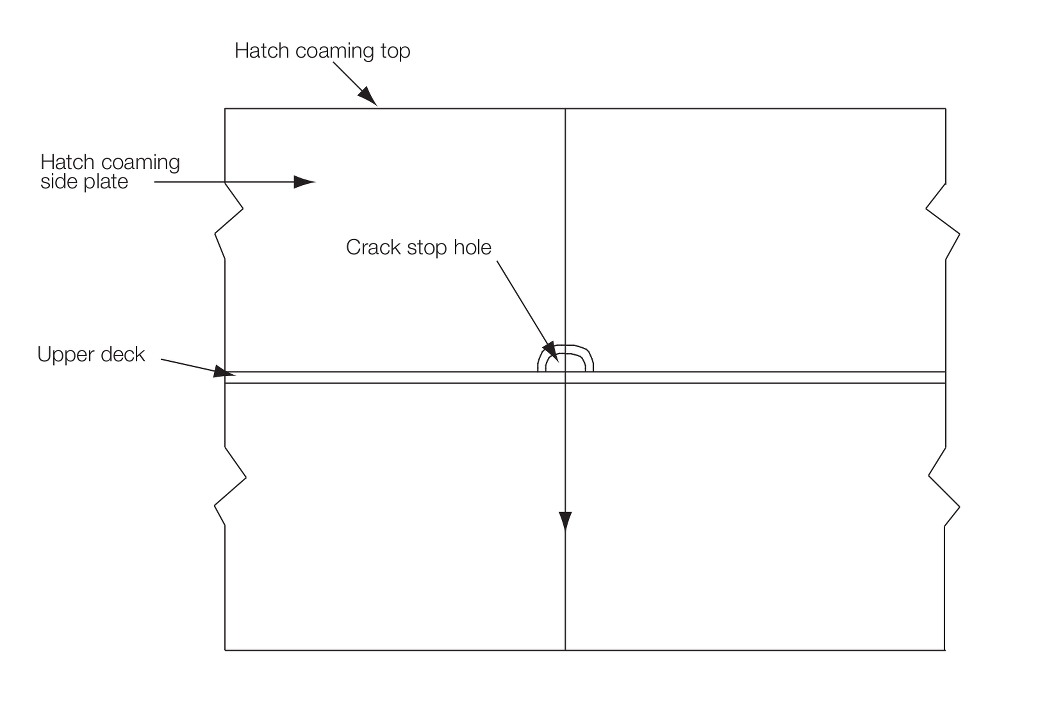
Figure 8.2.3 Crack arrest hole in way of the
block-to-block butt weld at the region where hatch side coaming weld meets the deck
weld
2.3.13 Where enhanced NDE is used to achieve Measure 3 see
Pt 4, Ch 8, 2.3 Requirements for use of thick steel plates 2.3.10.(d), the block to block butt welds of the hatch coaming side
plate, hatch coaming top plate and upper deck are to have a minimum crack tip opening
displacement (CTOD) value of 0,18 mm. The CTOD tests to confirm the CTOD value are to be
carried out to the satisfaction of LR.
2.3.15 The weld joints between the hatch coaming side and the upper deck are to be partial
penetration welds approved by LR.
2.3.16 In the vicinity of ship block joints, alternative weld details may be used for the deck
and hatch coaming side connection, provided additional means for preventing the crack
propagation are implemented and agreed by LR in this connection area.
|